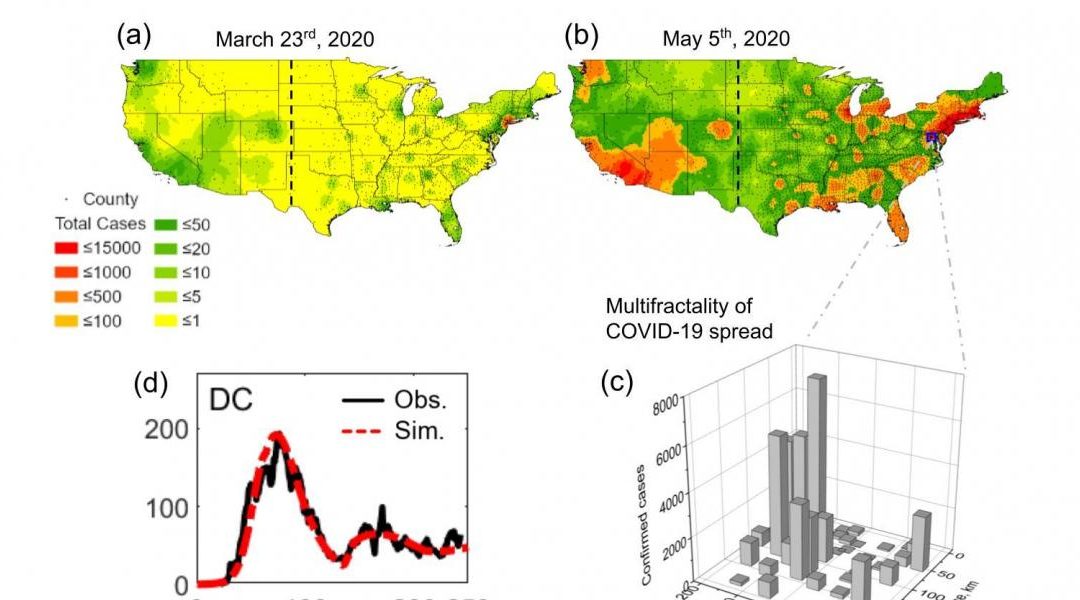
Early on in the COVID-19 pandemic, health officials seized on contact tracing as the most effective way to anticipate the virus’s migration from the initial, densely populated hot spots and try to curb its spread. Months later, infections were nonetheless recorded in similar patterns in nearly every region of the country, both urban and rural. A team of environmental engineers, alerted by the unusual wealth of data published regularly by county health agencies throughout the pandemic, began researching new methods to describe what was happening on the ground in a way that does not require obtaining information on individuals’ movements or contacts. Funding for their effort came through a National Research Foundation RAPID research grant (CBET 2028271). To read the full story.